Build a Stronger Upper Body and Sculpted Physique!
Are you ready to take your fitness journey to new heights?
Gorilla rows, the ultimate exercise for upper body strength and muscular development, are here to transform your physique. Discover the secrets behind the perfect form, explore targeted muscle engagement, unlock variations for an added challenge, and gain expert tips to maximize your results. Prepare to sculpt a powerful back, defined shoulders, and chiseled arms while improving posture and functional fitness.
It's time to unleash the beast within with Gorilla Rows!
Table of content
What Are Gorilla Rows?

Gorilla Rows are a variation of the traditional bent-over row, designed to target the upper and middle back muscles while also engaging the core and stabilizing muscles.
This exercise involves bending over at the hips while holding a weighted implement, such as a dumbbell, or kettlebell, and rowing it towards your body. The motion mimics the movement of a gorilla pulling something towards itself, hence the name "gorilla rows."
What is the Difference Between a Gorilla Row and a Bent Over Row?
The Gorilla Row is a dynamic, alternating single-arm row performed in a wide stance with more core and lower body engagement, while the Bent-Over Row is a static, bilateral row focused on lifting heavier weights with a more isolated back muscle focus.
Gorilla Row Muscles Worked
Gorilla rows are a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups in the upper body. Here are the primary and secondary muscles worked during gorilla rows:
Latissimus Dorsi (Lats): The lats are the largest muscles in the back and play a significant role in gorilla rows. They are responsible for the pulling motion as you row the weight towards your body.

Rhomboids: Located between the shoulder blades, the rhomboids stabilize the scapulae and assist in retracting them during the rowing movement.
Rear Deltoids: The rear deltoids, or posterior deltoids, are the muscles at the back of the shoulder. They are activated during gorilla rows to help pull the weight towards the body.
Biceps Brachii: The biceps brachii, located in the upper arm, act as synergists during gorilla rows. They assist the back muscles in pulling the weight towards the body.

Forearm Muscles: The muscles of the forearm, including the brachialis and brachioradialis, are engaged to grip and hold the weight during the exercise.
Lower Back Muscles: The erector spinal muscles of the lower back play a stabilizing role during gorilla rows, helping to maintain proper posture and alignment.
Core Muscles: The muscles of the core, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, are engaged to stabilize the torso throughout the exercise.
How to Do Gorilla Rows
Equipment needed: Dumbbells, or kettlebells
Starting Position: Stand with your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell in each hand with an overhand grip. Bend your knees slightly and hinge at the hips, lowering your torso until it’s almost parallel to the floor. Keep your back flat and your core engaged.
Grip and Setup: Let the weights hang down at arm’s length, directly below your shoulders. Your palms should face each other, and your head should be in a neutral position, aligned with your spine.
Rowing Motion: Begin the movement by pulling one weight up towards your ribcage, keeping your elbow close to your body. Squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top of the movement.
Lowering the Weight: Slowly lower the weight back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout. As you lower the first weight, begin pulling the opposite weight towards your ribcage.
Alternate Sides: Continue alternating rows, ensuring that each movement is controlled and deliberate.
Breathing: Exhale as you row the weight up and inhale as you lower it back down.
Benefits of Gorilla Rows
Upper Body Strength: Gorilla rows are a compound exercise that targets several major muscle groups, including the back, shoulders, and arms. By regularly performing gorilla rows, you can build significant upper body strength and increase your overall power.

Muscular Development: The exercise primarily targets the latissimus dorsi (lats), rhomboids, rear deltoids, and biceps. By consistently challenging these muscles with gorilla rows, you can promote muscular development and achieve a more sculpted and defined upper body appearance.
Posture Improvement: Gorilla rows are effective for improving posture by strengthening the muscles that support proper spinal alignment. The exercise targets the muscles of the upper back, which play a critical role in maintaining an upright posture and reducing the risk of rounded shoulders or a hunched back.
Core Engagement: While primarily targeting the upper body, gorilla rows also engage the core muscles as stabilizers. To maintain a stable and balanced position during the exercise, the muscles of the abdominals and lower back must work together, leading to improved core strength and stability.
Functional Fitness: Gorilla rows involve a pulling motion that mimics real-life movements, such as pulling or lifting objects. By training these movement patterns, you can enhance your functional fitness and make daily activities, such as lifting groceries or carrying heavy items, easier and more efficient.

Versatility and Accessibility: Gorilla rows can be performed with various equipment options, such as barbells, dumbbells, or kettlebells, making them accessible to individuals with different levels of strength and access to equipment. Additionally, the exercise can be modified or scaled to suit different fitness levels and goals.
Increased Grip Strength: Holding and rowing the weighted implement during gorilla rows requires a strong grip. Regularly performing this exercise can help improve grip strength, which can have benefits in various sports and daily activities that involve grasping and holding objects.
Variations and Progressions
Dumbbell Gorilla Rows

- Start by grabbing a dumbbell in each hand. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and knees slightly bent.
- Hinge forward at the hips while maintaining a neutral spine. Keep your back straight, chest up, and gaze forward. Your torso should be inclined at around a 45-degree angle to the floor. This position ensures proper engagement of the targeted muscles and minimizes strain on your lower back.
- Hold the dumbbells with your palms facing each other (neutral grip) and let your arms hang straight down in front of you. This is your starting position.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your torso and maintain a solid base throughout the exercise.
- Start the movement by pulling the dumbbells upward towards your lower chest or upper abdomen. Keep your elbows close to your body and focus on squeezing your shoulder blades together as you row. Exhale during this pulling phase.
- Pause for a brief moment at the top of the movement, ensuring a strong contraction of the back muscles.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position in a controlled manner while inhaling.
Single-Arm Gorilla Rows

- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and knees slightly bent.
- Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell in one hand with a neutral grip (palms facing in).
- Hinge forward at the hips, maintaining a neutral spine and a 45-degree angle with your torso.
- Rest your non-working hand on a stable surface for support.
- Engage your core muscles for stability.
- Pull the weight upward towards your lower chest or upper abdomen, keeping your elbow close to your body and focusing on squeezing your shoulder blade.
- Pause briefly at the top of the movement, feeling the contraction in your back muscles.
- Lower the weight back down in a controlled manner.
Resistance Band Gorilla Rows

- Begin by securing the resistance band to a sturdy anchor point, such as a door frame or a squat rack.
- Stand facing the anchor point with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hold the resistance band handles, or the band itself, with your palms facing each other (neutral grip).
- Take a step or two back to create tension in the band, ensuring it is securely anchored.
- Hinge forward at the hips, maintaining a neutral spine and a 45-degree angle with your torso.
- Keep your arms extended in front of you with a slight bend in your elbows. This is your starting position.
- Engage your core for stability and maintain a strong, upright posture.
- Pull the resistance band handles towards your lower chest or upper abdomen, squeezing your shoulder blades together.
- Pause briefly at the top of the movement, feeling the contraction in your back muscles.
Common Mistakes
When performing gorilla rows, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can compromise form and hinder the effectiveness of the exercise. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Rounded Back: One of the most common mistakes is rounding the back during the movement. This can place excessive stress on the lower back and increase the risk of injury. Instead, focus on maintaining a neutral spine throughout the exercise, keeping your back straight and avoiding any excessive rounding or arching.
Using Excessive Momentum: Swinging or using momentum to lift the weight can take the emphasis off the targeted muscles and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise. It's crucial to perform gorilla rows with controlled and deliberate movements, focusing on the muscles you're intending to work.
Pulling with the Arms Only: Gorilla rows primarily target the back muscles, but some individuals make the mistake of relying too much on their arms to perform the movement. Remember to initiate the rowing motion by engaging your back muscles and squeezing your shoulder blades together. The arms should act as secondary movers, assisting the back muscles in the pulling motion.
Incorrect Grip or Hand Placement: Using an improper grip or hand placement can affect the engagement of the target muscles. Ensure that your grip is secure and comfortable, and experiment with different hand positions (pronated, supinated, mixed) to find the one that works best for you and targets your muscles effectively.
Lifting Too Heavy: It's essential to choose a weight that allows you to maintain proper form and technique throughout the exercise. Lifting weights that are too heavy can compromise your form, increase the risk of injury, and limit the range of motion. Gradually increase the weight as you progress and feel confident in your form and strength.
Neglecting Core Stability: Your core muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing your torso during gorilla rows. Neglecting core engagement can lead to a loss of stability and compromise your form. Remember to activate your core muscles by bracing your abs and maintaining a stable and strong core throughout the exercise.
Not Allowing for Full Range of Motion: To maximize the benefits of gorilla rows, it's important to perform the exercise through a full range of motion. Ensure that you fully extend your arms at the bottom of the movement and pull the weight up until your elbows are close to your body at the top. Avoid shortening the range of motion, as it limits the activation of the target muscles.
Gorilla Rows for Different Fitness Goals
Muscle Building: Focus on moderate to heavy weights with a rep range of 8-12, emphasizing the mind-muscle connection and controlled movements.
Strength Development: Use heavier weights with lower reps (4-6) and longer rest periods between sets.
Endurance: Incorporate higher rep ranges (15-20) with lighter weights, or try timed sets to improve muscular endurance.
Fat Loss: Include Gorilla Rows in high-intensity circuit training or superset them with cardio exercises for a metabolism-boosting workout.
Back Exercises To Pair With Your Gorilla Rows
1. Pull-Ups

- Muscles Targeted : Latissimus dorsi, biceps, rhomboids, trapezius
- Why It Pairs Well : Pull-ups focus on vertical pulling, which complements the horizontal pulling motion of Gorilla Rows. Together, they provide a comprehensive workout for the upper and middle back.
2. Deadlifts

- Muscles Targeted: Lower back, glutes, hamstrings, traps
- Why It Pairs Well: Deadlifts target the lower back and posterior chain, balancing the upper and middle back focus of Gorilla Rows. This combination helps strengthen the entire back.
3. Bent-Over Rows

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, rhomboids, traps, rear deltoids, biceps
- Why It Pairs Well: Bent-over rows share a similar movement pattern with Gorilla Rows but can be performed with different equipment or grips to target the muscles differently. Using both in a routine can maximize back development.
4. Lat Pulldowns
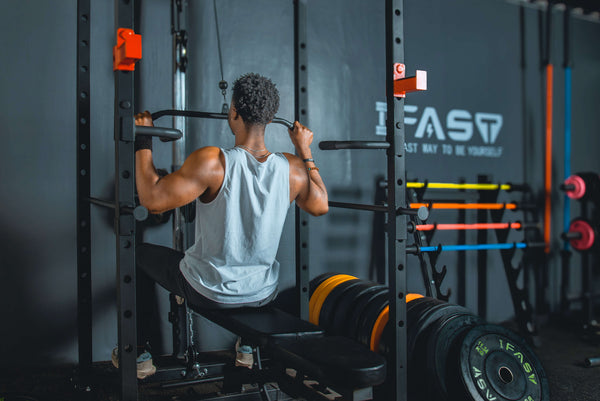

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, traps, rhomboids, biceps
- Why It Pairs Well: Lat pulldowns are an effective isolation exercise that emphasizes the lats, complementing the compound movement of Gorilla Rows.
5. Face Pulls

- Muscles Targeted: Rear deltoids, traps, rhomboids
- Why It Pairs Well: Face pulls are excellent for targeting the rear deltoids and traps, helping to improve shoulder health and posture. Pairing them with Gorilla Rows ensures that all areas of the back are addressed.
6. T-Bar Rows

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, rhomboids, traps, rear deltoids
- Why It Pairs Well: T-bar rows provide another variation of horizontal pulling, allowing you to switch up your routine while still focusing on building back thickness.
7. Single-arm Dumbbell Rows

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, rhomboids, traps, rear deltoids, biceps
- Why It Pairs Well: Single-arm dumbbell rows allow for unilateral training, helping to correct imbalances between the sides of your back. Pairing these with Gorilla Rows adds variety and balance to your back routine.
8. Inverted Rows

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, rhomboids, traps, rear deltoids, biceps
- Why It Pairs Well : Inverted rows are a bodyweight exercise that targets similar muscles as Gorilla Rows but with a different intensity and angle. This provides a great balance in your back workout.
9. Seated Cable Rows

- Muscles Targeted: Lats, rhomboids, traps, rear deltoids
- Why It Pairs Well: Seated cable rows allow for controlled, focused pulling that targets the middle back. Pairing this with the more dynamic Gorilla Rows can help fully develop the back muscles.
10. Hyperextensions

- Muscles Targeted: Lower back, glutes, hamstrings
- Why It Pairs Well: Hyperextensions focus on the lower back, complementing the upper and middle back emphasis of Gorilla Rows. This exercise ensures a balanced back routine that strengthens the entire posterior chain.
Sample Workout Routine
Warm-Up:
5-10 minutes of light cardio (e.g., rowing, cycling)
Dynamic stretching focusing on the back, shoulders, and hips
Workout:
Gorilla Rows: 4 sets of 10-12 reps per side
Pull-Ups: 4 sets of 8-10 reps
Deadlifts: 3 sets of 6-8 reps
Face Pulls: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
Single-Arm Dumbbell Rows: 3 sets of 10-12 reps per side
Inverted Rows: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
Hyperextensions: 3 sets of 15 reps
Cool Down:
5-10 minutes of stretching focusing on the back, shoulders, and hamstrings
Consider foam rolling to release any tension in the muscles worked
FAQs
Are Gorilla Rows suitable for beginners?
While beginners can perform gorilla rows, it's essential to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form before increasing the challenge.
Can I use dumbbells or kettlebells for Gorilla Rows?
Both dumbbells and kettlebells can be used for gorilla rows. Kettlebells might offer a slightly different feel due to their shape.
Can I do Gorilla Rows if I have back pain?
If you have back pain, consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise. Proper form and gradual progression are crucial.
Can Gorilla Rows help with posture?
Yes, Gorilla Rows strengthen the upper and middle back muscles, which can improve posture by pulling the shoulders back and supporting a neutral spine.
Conclusion
In short, gorilla rows are a versatile and effective exercise that can help you achieve a strong, sculpted upper body. By mastering the proper form, understanding the targeted muscles, and exploring variations, you can leverage gorilla rows to enhance your strength, muscular development, and overall fitness. Incorporate this exercise into your routine and enjoy the benefits it brings to your physique and performance.